In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Well

213 Questions With Answers In Motion Science Topic
2
Nasa Wallops Flight Facility Sounding Rockets Program Office Code 810

Unbalanced Forces And Motion Video Khan Academy

Drag Force And Terminal Speed
Newton S Laws
When a rocket ship accelerating in outer space runs out of fuel, it.

In the absence of an external force a moving object well. Which of the following forces exists between objects even in the absence of direct physical contact?. The object will also move in a straight line in the absence of a net external force. Net External Force = 0 ⇒A cm = 0 ⇒ V cm = constant.
They collide with each other at t=0. The liquid will then strive to obey these forces, spreading out as much as possible over the surface of the object and coating it with a more or less thick layer. We state that the surroundings exert a force on the object studied.
C) in the absence of an external force d) in all of the preceding cases. D) An object's velocity will only be in the direction of the net force exerted on it. I) Force can stop a moving object.
Newton's First Law of Motion is also known as the Law of Inertia. In the absence of an unbalanced force, an object at rest will start moving and an object in motion will stay in motion. If only one force acts upon an object, then this one force would be the net force.
Slide 2 / 51 2 When a cat sleeps on a table, the net force on it is A zero B directed upward C directed downward. The straight line motion in the absence of the constraining force is an example of Newton's first law.The example here presumes that no other net forces are acting, such as horizontal motion on a frictionless surface. So for an object to be in motion no force is required.
It is the property of mass of the body which opposes a change. When two objects collide the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision (in the absence of. V cm = 0 for t i < t < t f.
Iii) Force can change the direction of a moving body. B) slow down and eventually come to a stop. Login to reply the answers Post;.
The presence of unbalanced forces must always be associated with acceleration, not mere motion. " You will get an idea from the following explanation , Let us imagine a force F acts on a body of mass. Earth is moving in the absence of external forces due to conservation laws.
Slow down and eventually come to a stop d. Similarly, force experienced by B is. The two fundamental laws of physics are the conservation of energy and momentum.
An object's velocity will only remain constant in the absence of any forces or if the forces that act on it cancel each other out, i.e. Log in for more information. It states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force.
Gradually speed up until it reaches its terminal velocity e. See page 93 of the text. V) Force can change the speed of a moving body.
A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. Though it does not sound like the same answer, one can say that any process that. A) If a single force acts on an object, the object accelerates.
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net external force acti ng on the object and inversely. Move with constant velocity for a while and then slow to a stop. Updated 2 days ago|8/30/ 9:05:36 PM.
(e) If an object isn’t accelerating, no external force is acting on it. (b) If an object isn’t moving, no external forces act on it. It is a consequence of the law of conservation of energy angular momentum is conserved, such that mvrmr2 constant If an object is held to move in a circular path (an.
FORCE AND MOTION - 1. When an object all of a sudden changes its velocity and/or direction, we can always find an interaction between that object and its surroundings that is responsible for this change. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A) stop immediately.
In the absence of a force, a moving object will:. In the absence of external forces a moving object will a move with constant from PHY 105 at Gordon College. In the absence of external forces, the total momentum of a system is not altered by a collision.
Along an Einstein Geodesic. Move with constant velocity in a straight line b. C) continue moving at the same speed.
Move with constant velocity in a circular orbit c. B) come to an abrupt halt. In%the%absence%of%an%external%force,%amoving%objectwill% (A)%stop%immediately%%%%%(B)%slow%down%and%eventually%come%to%astop% (C)%move%faster%and%faster%%%%%(D.
Or, That is, total momentum before collision is equal to total momentum after collision if no external forces act on them which proves the principle of conservation of linear momentum. C) go faster and faster. Move with constant velocity.
It can be moving at constant speed. 2) In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A) stop immediately B) slow down and eventually come to a stop C) go faster and faster D) move with constant velocity. If no external forces are acting on a moving object, it will.
Login to reply the. Force causes objects to start moving. When an object experiences pure rotational motion about its center of mass, all of its points move at right angles to the radius in a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation with a speed proportional to the distance from the axis of rotation….
The net force can not come. Well, sort of - it’s somewhat correct to say it is inertia, and somewhat correct to say it isn’t. Give one example each where:.
There are kinds of friction in space. 1)In the absence of any net external force a moving object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line.This is also known as t view the full answer Previous question Next question. If air resistance is negligible, the net force on a falling object is the gravitational force, commonly called its weight w.
(a) An object can move even when no force acts on it. Momentum is of interest during collisions between objects. In the absence of any forces, no force is required to keep an object moving.
The string must provide the necessary centripetal force to move the ball in a circle. Then you stop the force and the object will keep moving at that speed. If the net force on an object is not zero, then the object will show a change in velocity.
1 In the absence of a net force, a moving object will A slow down and eventually stop B stop immediately C turn right D move with constant velocity E turn left. Forces exchanged by the particles in the system. B) a force stops a.
This is how rocket propulsion works -- a rocket throws exhaust gas in one direction and gets a push in the other. False - An object which is moving to the right could have unbalanced forces, but only if it is accelerating. A) move slower and slower until it finally stops.
When the rocket engines on the starship NO-PAIN-NO-GAIN are suddenly turned off, while traveling in empty space, the starship will. When an object is dropped, it accelerates toward the center of Earth. D) The body has some.
You only need a net force to change its speed. This process is governed by the conservation of momentum. Forces caused by external agent outside of the system.
The last instant just before an airplane crashes a passenger jumps out the door and falls only two feet to the ground. 4) A gun recoiling when it is fired is an example of. Ii) Force can move a resting object.
Under the influence of a force, an object will accelerate. Eventually come to a stop. When a force is applied to an object, it accelerates.
Similarly, if the object is at rest, it will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. D) none of the above. (d) If an object accelerates, at least one force is acting on it.
To give you a better idea, let’s consider a simple example. But there is some truth to what you were told. 5) A heavy object and a light object have the same momentum.
If no force tries to slow the object, it will keep moving forever (no forces needed for that). B) Following are the effects of force:. The net force adds up to zero.
In the absence of a force, a moving object will:. Speed increases and then decreases E. In the absence of forces, ("body") at rest will stay at rest, and a body moving at a constant velocity in a straight line continues doing so indefinitely.
C) If an object is accelerating, a force is acting on it. E) It is impossible to have motion in the absence of a force. Speed decreases and then.
Such as from zero to 1m/s. A) a force moves a stationary body. D) move with constant velocity.
B) An object in uniform motion in the absence of external force continues to move in the same direction. “Inertia” generally refers to the tendency of objects to continue moving in a straight line with a fixed velocity unless an external force is applied to them. If the net force on an object is zero, then the object experiences no velocity change.
In the absence of friction, gravity, and all other external forces, what kind of speed will an object display if it travels from the bottom to the top of an inclined plane?. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will do What?. In the absence of an unbalanced force, an object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion.
One has to be precise with language!. However, the momentum of an. If no external forces act on a moving object, it will?.
Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless an external force acts upon it. In physics, a force is any interaction that, when unopposed, will change the motion of an object.A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (which includes to begin moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate.Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. FALSE - To say that momentum is a conserved quantity is to say that if a system of objects can be considered to be isolated from the impact of net external forces, then the total momentum of that system is conserved.
Newton’s second law states that a net force on an object is responsible for its acceleration. This is what Newton's First law states " A body remains in a state of rest or uniform motion, unless it is acted upon by an external force. Once it starts moving, it will continue to do so until external forces act on it.
B) If an object isn't moving, no external forces act on it. Continue moving in a straight line. Objects in space can also fall apart into several pieces, turning one stationary object into a whole bunch of moving ones.
We have two hockey pucks sliding across a frictionless surface, and we neglect air resistance for simplicity. Asked 9/17/16 7:36:59 PM. According to Newton's third law of motion, the force experienced by A and B are equal and opposite,.
That, in the absence of external forces (torques), R 1 r1 r2 2 The conservation of angular momentum The quantity mvr(mr2) is called angular momentum. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will stop immediately. C) Rate of change of momentum is equal to the net force applied.
Accordingly for example, water in only a partially filled bottle will not occupy the bottom of the bottle, but, leaving the center empty, attempts to spread out over all the walls of. To make a body move from rest, external force is necessary. Lastly, this net force must be external to the object.
Search for an answer or ask Weegy. If the string breaks, the ball will move off in a straight line. A) conservation of momentum b) conservation of angular momentum c) conservation of energy d) none of the above.
While the child is walking along the slab the net external force is zero, then the the acceleration of the center of mass is zero is zero and the linear momentum of the system and the velocity of the center of mass are constant. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will a. In other words, Galileo stated that, in the absence of a force, a moving object will continue moving.
A moving object will slow and stop due to any force that acts in a direction opposite to the direction of motion. Iv) Force can change the shape of the body. Force causes objects to stop moving.
(c) If a single force acts on an object, the object accelerates. Move faster and faster. The acceleration a is in the direction of the force and proportional to its strength, and is also inversely proportional to the mass being moved.
Newton S First Law Of Motion Zona Land Education
4 2 Newton S First Law Of Motion Inertia Texas Gateway

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Module 3 Constrained Motion And Constraint Forces Per Wiki

Trajectory Wikipedia

The Physics Of Sports

Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces Physics

Forces And Motion Scripted

Chapter 4

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed
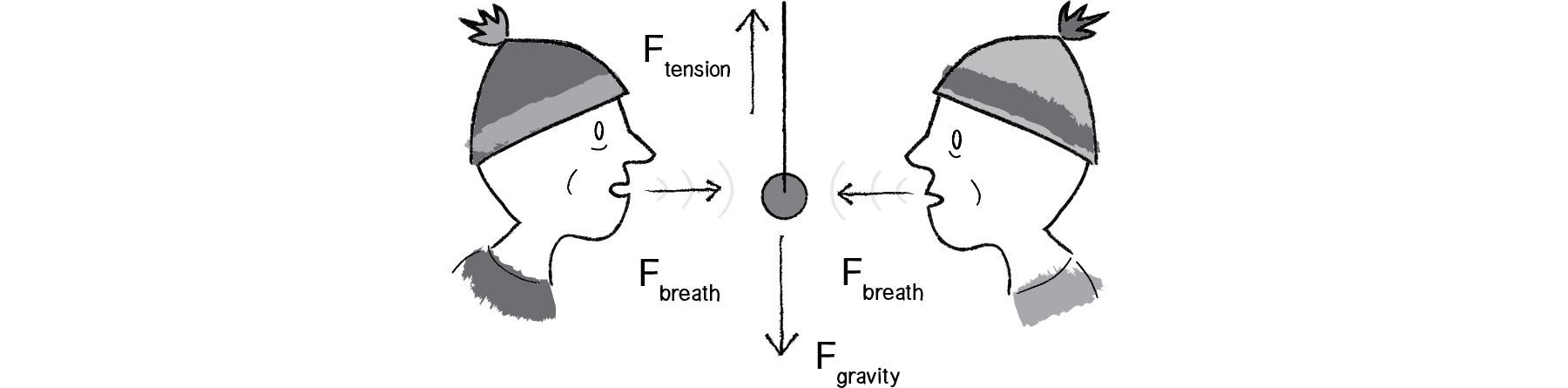
Newton S Laws Of Motion Article Forces Khan Academy

Mechanics Conservation Of Momentum Britannica

Rigid Body Wikipedia

Chapter 4

What Is Newton S Second Law Of Motion Isaac Newton The Guardian

Chapter 4

6 1 Solving Problems With Newton S Laws University Physics Volume 1
Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrs8r0lyjy0dpf Tpezn7gto9iif7tzdcw Sd1uxwu17jcmzzu Usqp Cau

Laws Of Motion Aristotle S Fallacy And Galileo S Observations Ppt Download
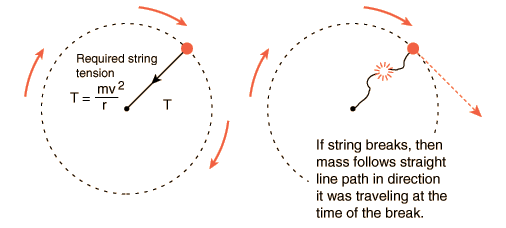
Newton S Laws

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Determining The Individual Forces Acting Upon An Object Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Cdn2 Hubspot Net Hubfs Human movement excerpt Pdf T
2

Centripetal Force Conservation Laws Newton S Laws And Kinematics Openstax Cnx

Newton S Second Law Of Motion Concept Of A System Physics

Drag Force And Terminal Speed

Q Tbn 3aand9gct8uds2cx1wtuq E1robvjb16iobpy Buqnq Usqp Cau

Reactive Centrifugal Force Wikipedia

Chapter 4

Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience

Biomechanics In Sport Physiopedia

Inertia And Mass

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed
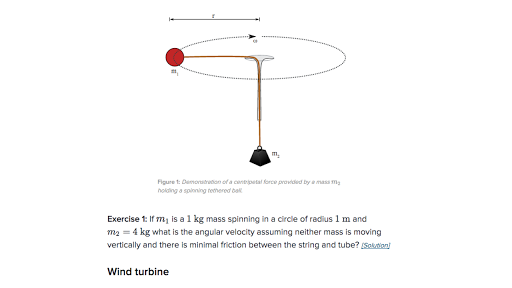
What Is A Centripetal Force Article Khan Academy

Nasa Wallops Flight Facility Sounding Rockets Program Office Code 810

Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces Physics
2

Chapter 4

Laws Of Motion Aristotle S Fallacy And Galileo S Observations Ppt Download
Newton S Laws

Force Mass Acceleration Newton S Second Law Of Motion Live Science

Drag Force And Terminal Speed

Giving Information Book Chapter Iopscience

Newton S Second Law Of Motion Concept Of A System Physics
The Impetus Theory In Judgments About Object Motion A New Perspective Springerlink
2

Mechanics Conservation Of Momentum Britannica

Giving Information Book Chapter Iopscience

Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience

Inertia And Mass

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Laws Of Motion Aristotle S Fallacy And Galileo S Observations Ppt Download

Analysis Of Situations In Which Mechanical Energy Is Conserved

Friction Wikipedia
Newton S First Law Of Motion Zona Land Education

Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq Ekss6fynnmh4ptmwzhja6yl87yzmnalomzxkliv6vfjkb9n Usqp Cau

External Force Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Chapter 4
Newton S Laws Of Motion Article Forces Khan Academy
2

Biomechanics In Sport Physiopedia

Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience
3
Internal Vs External Forces

Giving Information Book Chapter Iopscience
Arxiv Org Pdf 1810
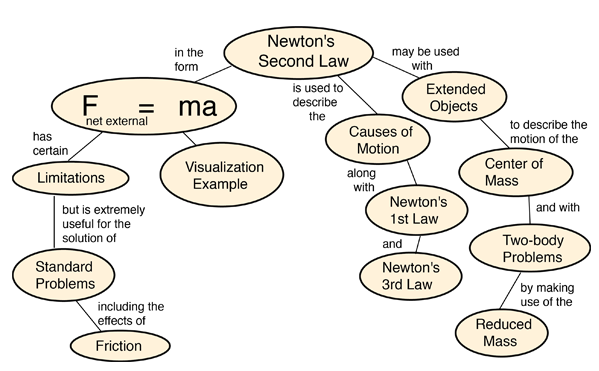
Newton S Laws

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Inertia The Force That Holds The Universe Together
1

Laws Of Motion Aristotle S Fallacy And Galileo S Observations Ppt Download

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Coriolis Force Wikipedia

Motion Under Gravity View As Single Page
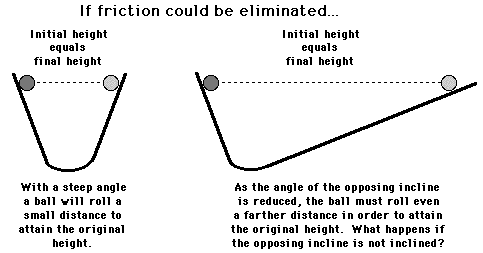
Inertia And Mass
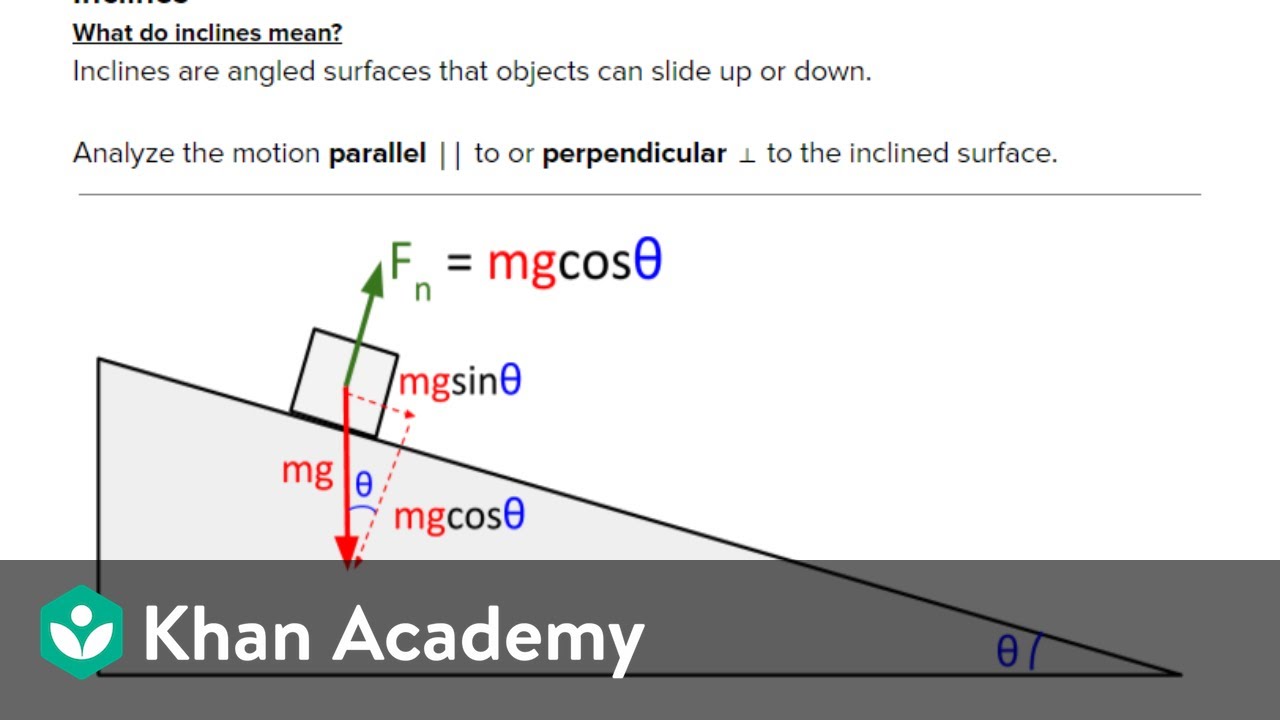
Ap Physics 1 Review Of Forces And Newton S Laws Video Khan Academy

6 3 Centripetal Force University Physics Volume 1

Unbalanced Forces And Motion Video Khan Academy

Normal Force And Contact Force Video Khan Academy

Chapter 4

Chapter 4

6 1 Solving Problems With Newton S Laws University Physics Volume 1
Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience

Chapter 4

Inertia And Mass

Chapter 4
Http Web Mit Edu Yczeng Public Workbook 1 full Pdf

Pdf Student Misconceptions About Force And Acceleration In Physics And Engineering Mechanics Education

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed
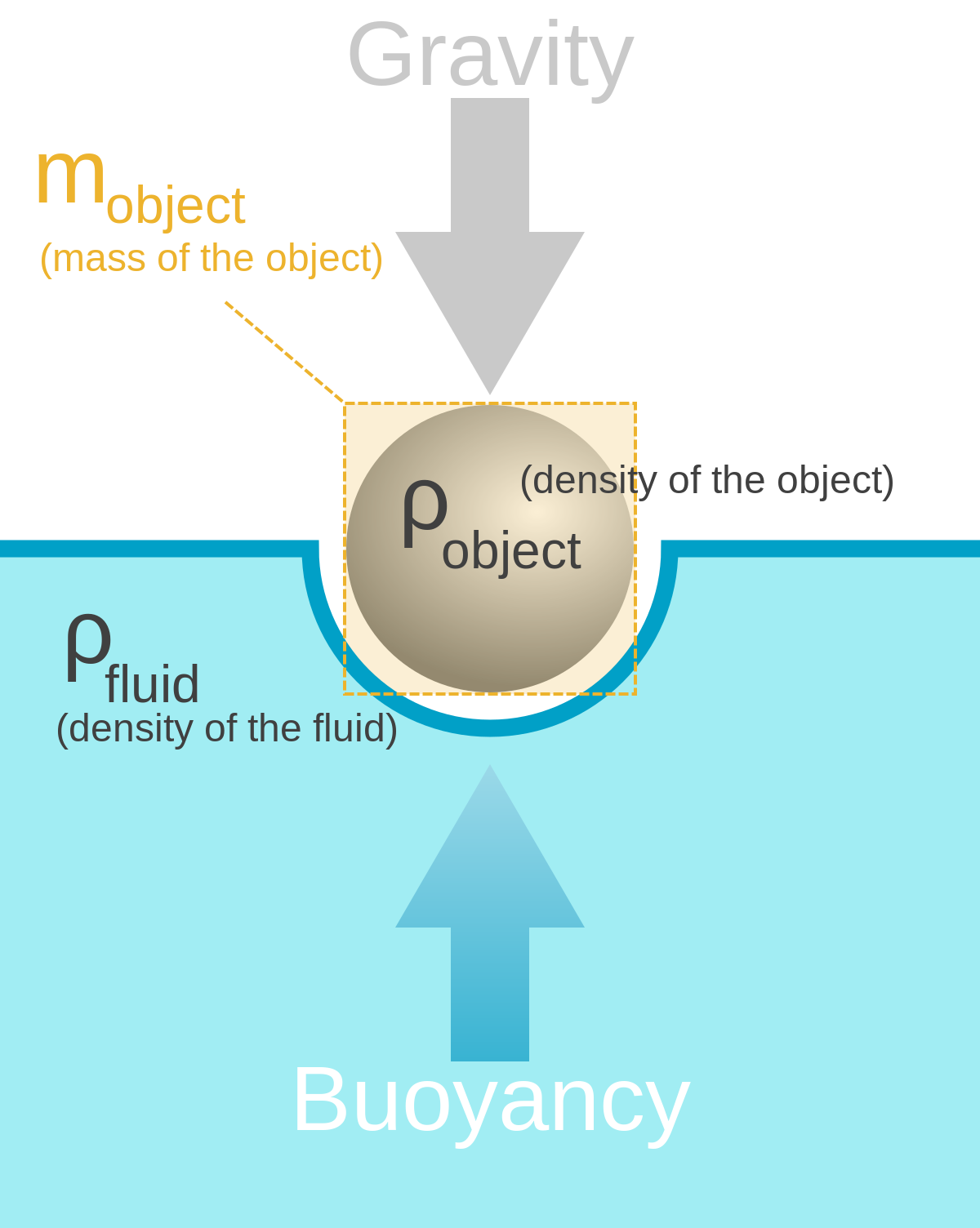
Buoyancy Wikipedia

Developing Mathematical Models Of Translating Mechanical Systems

Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces Physics
What Is Conservation Of Momentum Article Khan Academy

Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience



