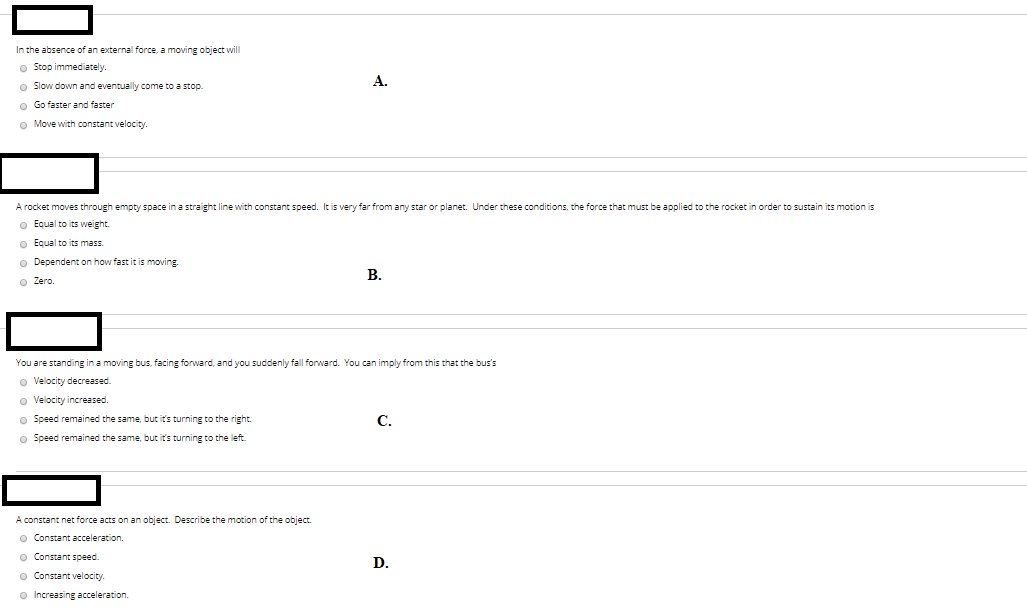
In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Will Move With Constant
Http Content Njctl Org Courses Science Ap Physics 1 Dynamics Dynamics 2 D Multiple Choice Dynamics 2 D Multiple Choice 14 06 10 Pdf

Giving Information Book Chapter Iopscience

Spm F4 Chapter 2 Notes Notes

Solved For General Projectile Motion The Horizontal Comp Chegg Com
Newton S Laws

Drag Force And Terminal Speed
E) move with constant velocity in a circular orbit.

In the absence of an external force a moving object will move with constant. Choice (a) is true. It is slowing down, or already stopped. The net force acting on the object is zero.
This means that if an object is moving along, untouched by a force of any kind, it will continue to move along in a perfectly straight line at a constant speed. 4) When the rocket engines on the starship NO-PAIN-NO-GAIN are suddenly turned off, while. Net External Force = 0 ⇒A cm = 0 ⇒ V cm = constant.
Newton's laws of motion help explain why an object needs a force to make it move. Constant Force and Constant Motion I see this problem all the time. If this force was absent, the object would fly of the tangent.
When a force is applied the velocity of the object changes from 0 to some velocity V (and it keeps increasing as long as the force is present). Inertia also explains this. (The tendency of objects to resist changes in motion was what Johannes Kepler had called inertia.) This insight was refined by Newton, who made it into his first law, also known as the "law of inertia"—no force means no acceleration, and hence the body will maintain its velocity.
O move with constant velocity for a while and then slow to a stop. And now instead of assuming that this block is stationary, let's assume that it's moving with a constant velocity. Net force = 0 Net force = 0 • An object can have many forces acting on it at the same time.
Tension in string weight of block Example:. Slow down and eventually come to a stop C. When a parachutist jumps from an airplane, he eventually reaches a constant speed, called the terminal velocity.
Unbalanced forces will cause objects to change their state of motion and a balance of forces will result in objects continuing in their current state of motion. 3) In the absence of an external force, a moving object will D) move with constant velocity. What type of path does a moving object follow in the absence of a force?.
Go faster and faster. According to newtons second law , the rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the net force exerted by it. Force has the following effects on objects.
In the absence of an external force, a moving object will a. And that's the normal force of the wedge on the block. A 4-kg object moving at 4 m/s c.
Move with constant velocity for a while and then slow to a stop. The manner in which objects will move is determined by the answer to this question. Typically, the reference point is the Earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used.
Inertia is one of the primary. The object will slow down at a constant rate until coming to rest. C) gradually speed up until it reaches its terminal velocity.
Asked by S.Strange on March 23, 10;. I think your confusion is that you believe that you need a force to keep an object moving at constant speed and that the object will stop if you do not keep doing a force upon it. Inertia comes from the Latin word, iners, meaning idle, sluggish.
There are various ways to say this.A moving object will slow and stop due to any. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to A. Move with constant velocity in a straight line b.
24) In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A) stop immediately. Thus the long cannon produces a larger momentum. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will O move faster and faster.
A book on the table is an example of a balanced force. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A. So now we're dealing with-- let me do that in a different color.
14) Which of the following objects has the largest kinetic energy?. A balanced force keeps an object moving at a constant velocity. The object will continue to move with a constant velocity.
The object will continue to move with a constant velocity. Another has a magnitude of 60.0N and is due west. An object is moving with constant velocity.
Momentum, on the other hand, explains some of the most important interactions in nature. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will a. An object that is moving does not need to be acted upon by an external force to stay in.
C) move slower and slower until it finally stops. In%the%absence%of%an%external%force,%amoving%objectwill% (A)%stop%immediately%%%%%(B)%slow%down%and%eventually%come%to%astop% (C)%move%faster%and%faster%%%%%(D. The only thing that can change either situation is the action of an unbalanced force on the object (i.e.
An electric potential (also called the electric field potential, potential drop, or the electrostatic potential) is the amount of work needed to move a unit of electric charge from a reference point to a specific point in an electric field without producing an acceleration. The object will stop moving immediately and remain at rest until acted on by a net force. This problem has been solved!.
8) An object is hanging by a string from the ceiling of an elevator. So that is going in that direction at 49 square roots of 3 newtons. 7) In the absence of external forces, a moving object will a) move with constant velocity.
A 6-kg object moving at 2 m/s. Gradually speed up until it reaches its terminal velocity. While the child is walking along the slab the net external force is zero, then the the acceleration of the center of mass is zero is zero and the linear momentum of the system and the velocity of the center of mass are constant.
D) Move With Constant Velocity. D) move with constant velocity in a straight line. (a) a stationary object to move, (b) a moving object to change its speed, (c) a moving object to change its direction of motion, (d) an object to change in size and shape.
When the rocket engines on the starship NO-PAIN-NO-GAIN are suddenly turned off, while traveling in empty space, the starship will. State the equilibrium rule for forces in symbolic notation. Slow down and eventually come to a stop.
Now if you remove the force, the object will move with the constant velocity V provided no other force is acting on it. The cause of acceleration may be due to the phenomena such as gravity and magnetism. Under these conditions the first law says that if an object is not pushed or pulled upon, its velocity will naturally remain constant.
O move with constant velocity. This means the object will not start to move spontaneously, without a push. A stationary object can have several forces acting on it, but if the vector sum of all these external forces is zero, there is no net force and the object remains stationary.
Once you stop the force the object will keep moving at a constant speed, so its acceleration and the net force upon it will be zero. What is the tension in the string?. The force of the book's weight is counteracted by the normal force (support force) of the table.
The acceleration a is in the direction of the force and proportional to its strength, and is also inversely proportional to the mass being moved. C) go faster and faster. B) slow down and eventually come to a stop.
Move faster and faster. It makes an object with mass to change its velocity. In The Absence Of An External Force, A Moving Object Will A) Go Faster And Faster.
Move with constant velocity. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight line at a constant speed, when no forces act upon them. This change in velocity is termed as acceleration.
In order for a block to be moving at a constant velocity, the forces. If a block is moving on a rough surface, and friction is the only force acting on it, it is not moving with a constant velocity. D) move with constant velocity.
Since the object is moving and has an absence of external force such as friction, drag force, air resistance, even gravitational force, etc., there is no way that the. 'an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity. An object at rest will stay at rest unless an external resultant force acts on it.Also an object will continue to move at constant velocity unless an external resultant force acts on it.Newton's.
In Physics, force is any movement that occurs on an object when an external object is acted upon it. To be in layman terms constant vel. 'unless it experiences a net external force'.
In the absence of an external force, a moving object will. 1)In the absence of any net external force a moving object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line.This is also known as t view the full answer. Move with a constant velocity.
It refers to the push or pull that cause an object with mass to accelerate. V cm = 0 for t i < t < t f. B) slow down and eventually come to a stop.
Gradually speed up until it reaches its terminal velocity e. When a net force is applied to an object at rest, it accelerates, and the reverse process has the same explanation. Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its velocity.This includes changes to the object's speed, or direction of motion.
The answer is letter "D". • If all the forces oppose each other exactly then the net force = 0 and the object will either be at rest or move with constant velocity. Move with a constant velocity in a straight line.
An object moving with constant velocity cannot exert net force because Justification:. Move with constant velocity in a cicular orbit. An 8-kg object moving at 2 m/s b.
If it is moving, it will continue to move at a constant speed in a straight line. In the absence of forces, ("body") at rest will stay at rest, and a body moving at a constant velocity in a straight line continues doing so indefinitely. B) slow down and eventually come to a stop.
The elevator is moving up at constant speed. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will stop immediately. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A.
A block hanging by. When a force is applied to an object, it accelerates. O slow down and eventually come to a stop.
Move with a constant velocity. This means the velocity stays constant with a value of zero. Move with constant velocity in a circular orbit c.
What must the magnitude and direction of the 3rd force, such that the object continues to move at a. One cforce has a magnitude of 80.O N and is directed due north. An object in motion continues to move at constant velocity in the absence of external forces.
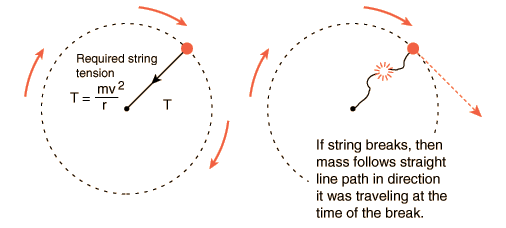
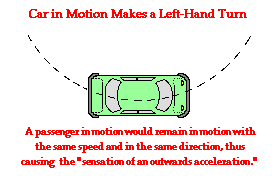
The force is constant. As centripetal force is making the object moving in circular path, in its absence the body will not be moving in a circular path and centrifugal force will act on it and it will move in a straight direction. In other words, Galileo stated that, in the absence of a force, a moving object will continue moving.
B) Slow Down And Eventually Come To A Stop. Which of the following best describes the force (s) acting on the object?. B) continue moving at the same velocity.
Anonymo2 anonymo2 The force acting on the body is centripetal force. Three forces act on a moving object. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A) stop immediately.
Slow down and eventually come to a stop. The acceleration of the object net force Example:. Since in the absence of any external forces, the inertia of a body will not allow it to change its state of motion making it go in a straight line.
Three forces act on a moving force object. The net force acting on it B. See full answer below.
Slow down and eventually come to a stop d. The most critical question in deciding how an object will move is to ask are the individual forces that act upon balanced or unbalanced?. To increase the momentum of the outgoing shell, the time of contact must increase.
If no external forces are acting on a moving object, it will A) continue moving at the same speed. The idea that if you apply a constant force on an object, it should move at a constant speed. What is the net force on a bag pulled down by gravity with a force of 18 newtons and pulled upward by a rope with a force of 18 newtons?.
C) move faster and faster. Choice (b) is also true. Force can make a stationary object move or make a moving object move faster A toy car can be made to move by giving it a little push.
The object will continue to move with a constant speed, traveling in a circular path. Go faster and faster D.

Forces And Newton S Laws Of Motion Ppt Download

Chapter 4
Newton S Laws

Solved 8 It Is Possible To Have Zero Acceleration And S Chegg Com

Newton S Laws Of Motion And Projectiles
2

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Q Tbn 3aand9gcqwp2nhsp2trtzutvth7povvulebuqzkf8w4g Usqp Cau
Dynamics Practice Problems

Giving Information Book Chapter Iopscience

Drag Force And Terminal Speed

Leonardo Da Vinci Cause Effect Linearity And Memory Sciencedirect
Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience

What Is The Direction Of Force Of Friction Acting On A Body Moving On A Fixed Surface

Newton S Second Law Of Motion Concept Of A System Physics

Solved In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Obje Chegg Com
What Is A Centripetal Force Article Khan Academy
Solved In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Obje Chegg Com
Http Web Mit Edu Yczeng Public Workbook 1 full Pdf

Physics For Scientists And Engineers 6e Ppt Download
Newton S Laws Of Motion Article Forces Khan Academy

Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces Physics

Centripetal Force Conservation Laws Newton S Laws And Kinematics Openstax Cnx

Dynamics Presentation 01 Youtube

Solved 1 5 In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Chegg Com
Newton S Laws Of Motion Article Forces Khan Academy

Forces And Motion Scripted

Solved Consider A System Consisting Of Two Blocks M 1 An Chegg Com
Why Is Horizontal Velocity Constant In Projectile Motion Socratic
2

Relative Velocity And Relative Acceleration Ppt Video Online Download

Forces And The Laws Of Motion Chapter 4 Forces And The Laws Of Motion 4 1 Changes In Motion Forces A Force Is A Physical Quantity That Can Affect Ppt Download

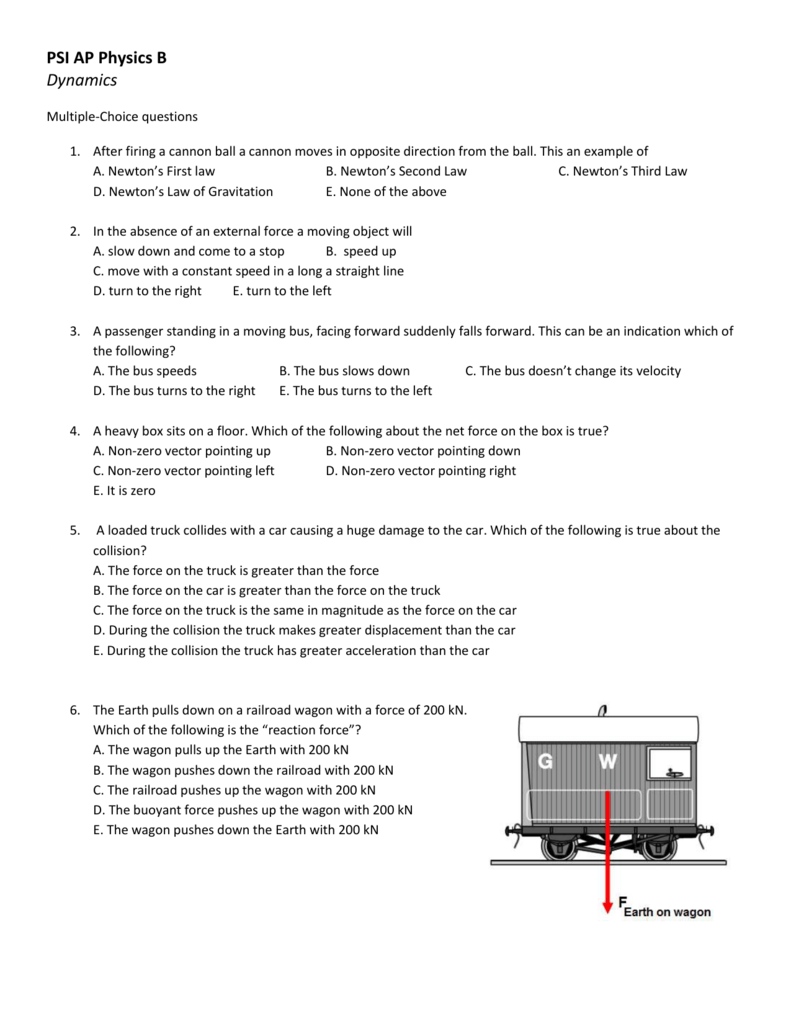
Psi Ap Physics B Dynamics

Spm F4 Chapter 2 Notes Notes
Cbse 9 Physics Cbse Work And Energy Ncert Solutions
The Centripetal Force Requirement

Physics 160 Dynamics Worksheet 1 Which Of Newton S Laws Best

Mechanics Conservation Of Momentum Britannica

Moving Round The Edi Uudiy I T Can There Be Displacement Of An Object In The Absence Of Any Force Acting On It Think Discuss This Question With Your Friends And Teacher

Ppt Force Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Solved Pre Lab Q1 The Introduction Defines Inertia As Th Chegg Com

Leonardo Da Vinci Cause Effect Linearity And Memory Sciencedirect

Multiple Choice Review Questions Weight Force

Newton S Laws Newton S Laws Siyavula
Forces Newton S Laws Of Motion Book Chapter Iopscience

Chapter 4

Giving Information Book Chapter Iopscience
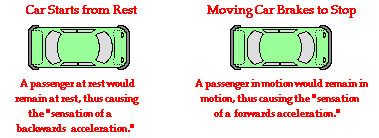
In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Will A S

Collins Cambridge International As A Level Physics By Collins Issuu
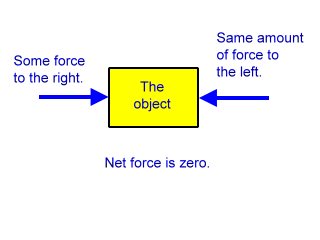
Newton S First Law Of Motion Zona Land Education

Solved 64 In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Chegg Com

Solved Test 2b General Physics I Physies 2110 03 94 Fall Chegg Com
Http Wbhsphysics Weebly Com Uploads 8 1 3 9 Ap C Forces Multiple Choice Pdf
Newton S Laws
Quick Quiz Prezentaciya Onlajn

Force Motion And Energy
.jpg)
Ask The Physicist

Chapter 4
2

Solved 16 A Ball Rolls Off The Edge Of A Table The Hori Chegg Com

Chapter 4

Solved In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Obje Chegg Com

Test Review Greenwich Public Schools

Unbalanced Forces And Motion Video Khan Academy

In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Will A Stop Immediately B Slow Down And Brainly Ph

Coriolis Force Wikipedia
The Centripetal Force Requirement
2

Newton S Second Law Of Motion Concept Of A System Physics

Solved I Need Help With These Three Can Anyone Go Into D Chegg Com

Solved In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Obje Chegg Com

Chapter 4 The Laws Of Motion Phy 53 Conceptual Questions Phy 53 Conceptual Questions Ppt Download
Centripetal Force Elvis Rowan Edu
Buoyancy Wikipedia

Chapter 4

4 3 Newton S Second Law Of Motion Concept Of A System Texas Gateway

Spm F4 Chapter 2 Notes Notes
Physicsgg Files Wordpress Com 19 01 300 Creative Physics Problems With Solutions Ce 92 Pdf
2

Physics Principles And Applications 6e Giancoli Chapter 4 Dynamics Newton S Laws Of Motion Pdf Free Download

Chapter 5 The Laws Of Motion Ppt Download

Fisika Chapter 5 The Law Of Motion Part 1

Chapter 4
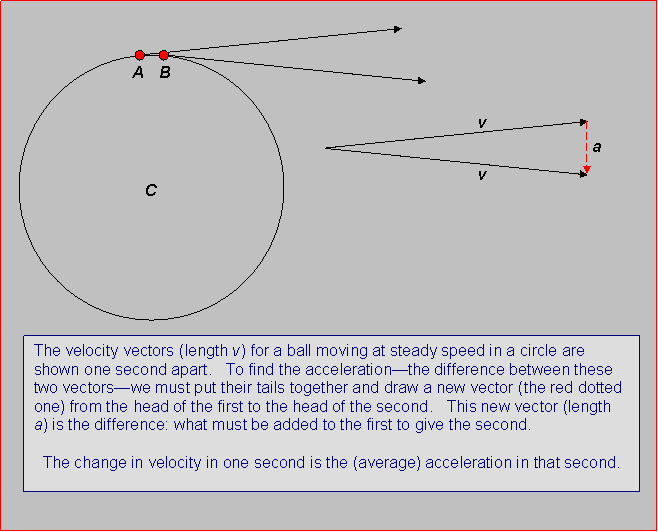
Newton S Laws

Chapter 4

Solved Question 3 In The Absence Of An External Force A Chegg Com

Exam Name Multiple Choice Choose The One Alternative That
2

Chapter 5 The Laws Of Motion Pdf Free Download
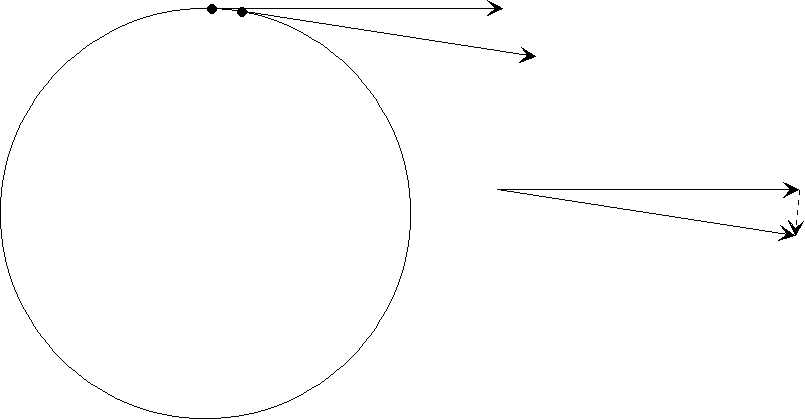
Newton S Laws

Pdf Student Misconceptions About Force And Acceleration In Physics And Engineering Mechanics Education

Newton S First Law Of Motion Newton S First Law Is Often Called The Law Of Inertia Newton S First Law Of Motion States An Object At Rest Will Remain Ppt Download
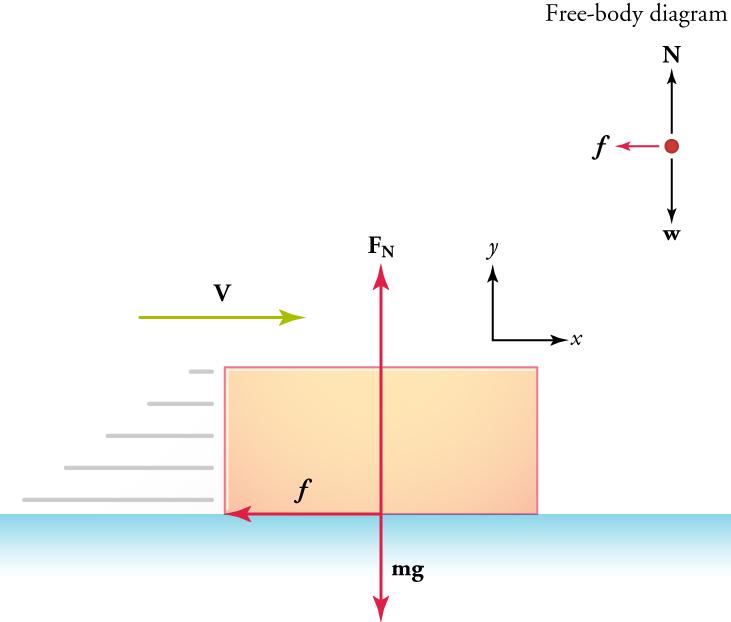
4 2 Newton S First Law Of Motion Inertia Texas Gateway
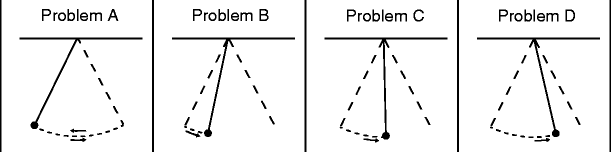
The Impetus Theory In Judgments About Object Motion A New Perspective Springerlink



