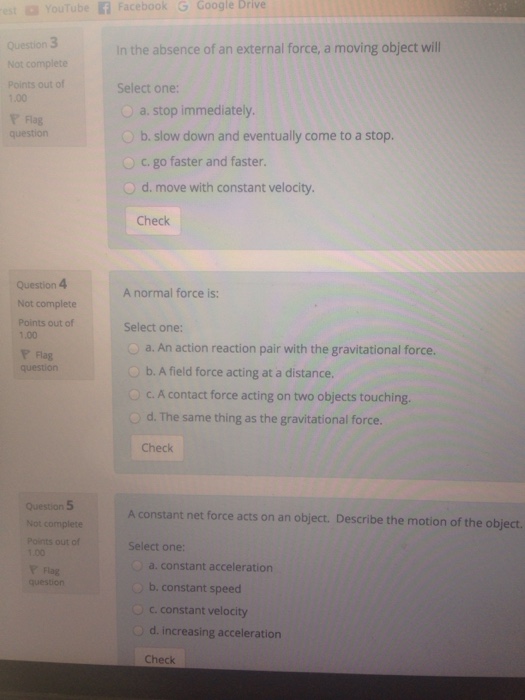
In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Will Blank

8 3 Elastic And Inelastic Collisions Texas Gateway
Newton S Laws Of Motion Article Forces Khan Academy
Http Www Edudel Nic In Welcome Folder Support Material 16 17 11 Sm 11 Physics Eng 1617 Pdf

The Graph Describes The Motion Of An Object The Object Moves With From A To B It Remains From Brainly Com
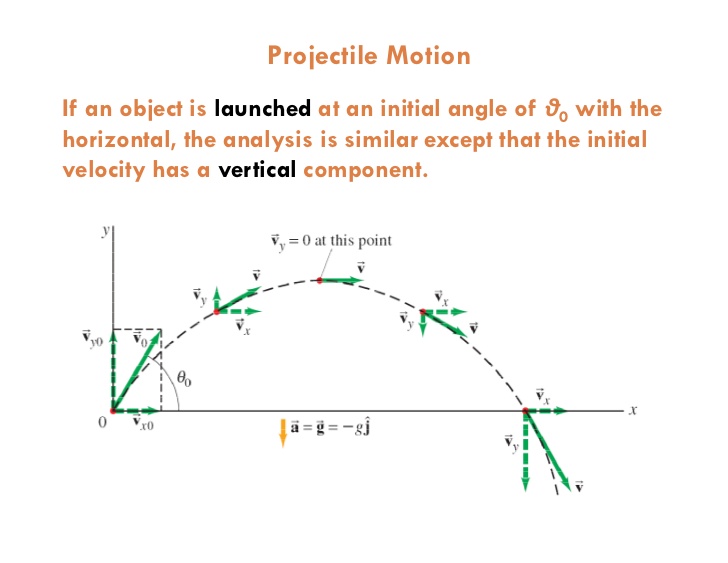
Why Is Horizontal Velocity Constant In Projectile Motion Socratic
Eq Uen Org Emedia File e7a 1990 4eb8 A075 17c5302a69ff 1 Physicsrs Pdf
The answer is letter "D".

In the absence of an external force a moving object will blank. If the net force on an object is zero, then the object experiences no velocity change. C) Rate of change of momentum is. The first law states that if the net force (the vector sum of all forces acting on an object) is zero, then the velocity of the object is constant.
FORCE AND MOTION - 1. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will a. E) It is impossible to have motion in the absence of a force.
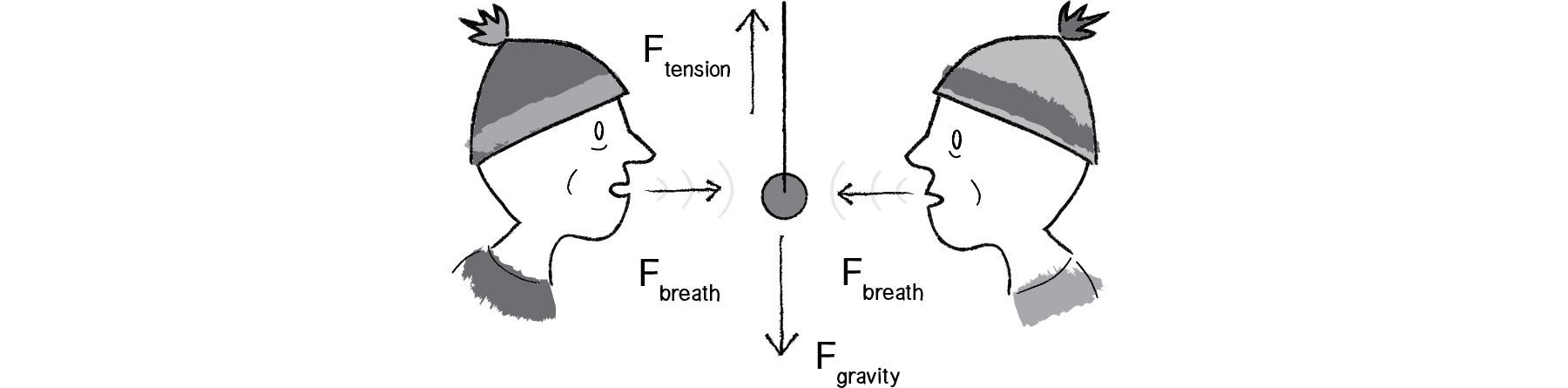
Force is not something an object has). 8) An object is hanging by a string from the ceiling of an elevator. D) move with constant velocity.
7) In the absence of external forces, a moving object will a) move with constant velocity. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net external force acti ng on the object and inversely. Force causes objects to stop moving.
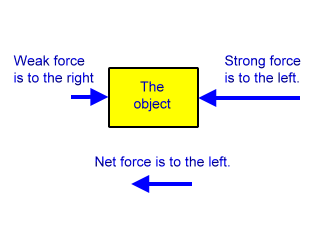
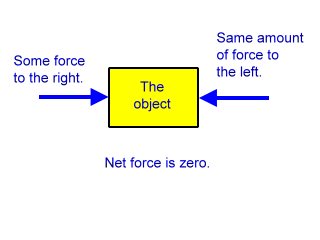
Centrifugal Force The force experienced by all objects in a rotating coordinate system that seems to pull them away from the center of rotation. Two equal and opposite forces have the same effect, they cancel to create zero net force. If the net force on an object is not zero, then the object will show a change in velocity.
That force, which is resisting motion, is friction. Therefore, the statement that the object's velocity is constant is a statement that both its speed and the direction of its motion are constant. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight line at a constant speed, when no forces act upon them.
In the absence of the force of gravity, a rock thrown into the air will move away from the center of the Earth and never fall back. D) An object's velocity will only be in the direction of the net force exerted on it. Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force.
An object's velocity will only remain constant in the absence of any forces or if the forces that act on it cancel each other out, i.e. When a force is applied to an object, it accelerates. Lastly, this net force must be external to the object.
That Is, Acceleration Is The Derivative. The law implies that the smallest net force on the object will move it. The resistance to motion can also occur when the object is at rest.
In the absence of all forces (gravity, friction, air resitance) a moving object has no reason to stop and so will carry on. C) move faster and faster. It is simply a quantity which proves to be useful in the analysis of situations involving forces and impulses.
It may have forces acting on it, but as forces are vectors they can cancel each other. Oxygen), or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms (e.g. Internal forces are forces exchanged by the objects in the system.
In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A) stop immediately. For example, if an apple is dropped from the branch of a tree, the force of gravity does work to move (accelerate actually) the apple from the branch to the ground. “Inertia” generally refers to the tendency of objects to continue moving in a straight line with a fixed velocity unless an external force is applied to them.
Essentially, moving a force from point A to B (as shown above) requires creating an additional couple moment. If it is moving, then it has kinetic energy. And if an object has kinetic energy, then it definitely has mechanical energy.
C) go faster and faster. Slide 2 / 51 2 When a cat sleeps on a table, the net force on it is A zero B directed upward C directed downward. Also called the law of inertia, this is the most important thing to realize about motion.
Only external forces affect the motion of a system, according to Newton’s first law. These concepts are independent of the type of force. B) continue moving at the same velocity.
So the same principal also applies to. Objects do not have force (i.e. Fictitious forces do not arise from an external object like genuine forces do, but rather as a consequence of trying to keep up with an accelerating environment.
There are various ways to say this.A moving object will slow and stop due to any. This and Newton's other laws are hard to observe on Earth, where gravity and friction play a part on moving objects. Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its velocity.This includes changes to the object's speed, or direction of motion.
If no external forces are acting on a moving object, it will A) continue moving at the same speed. Momentum is NOT a form of energy;. Since the object is moving and has an absence.
A) Equal and opposite reaction force acts for each action. When an object all of a sudden changes its velocity and/or direction, we can always find an interaction between that object and its surroundings that is responsible for this change. For instance, if a.
B) slow down and eventually come to a stop. 2) In the absence of an external force, a moving object will A) stop immediately B) slow down and eventually come to a stop C) go faster and faster D) move with constant velocity. But these two forces alone have a zero resultant, which means that there is o net force on the object.
If an object isn't moving, no external forces act on it. If an object accelerates, a force is acting on it. Inertia comes from the Latin word, iners, meaning idle, sluggish.
Inertia is one of the primary. In the absence of external forces or torques acting on an object or system of objects, the total momentum of a system will remain constant. We state that the surroundings exert a force on the object studied.
A noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. In the case of the Earth it is moving in several different ways. The normal force can be less than the object’s weight if the object is on an incline, as you will see in the next example.
When a net force is applied to an object at rest, it accelerates, and the reverse process has the same explanation. If a force acting on a moving object is no longer acting on that object, the object's inertia will keep it moving the way it was when the action of the other force was withdrawn. Under the influence of a force, an object will accelerate.
An object's energy and momentum can only be change by applying an external force. " You will get an idea from the following explanation , Let us imagine a force F acts on a body of mass. (As referring to an inelastic collision, in contrast to an elastic.
That, in the absence of external forces (torques), R 1 r1 r2 2 The conservation of angular momentum The quantity mvr(mr2) is called angular momentum. When two objects collide the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision (in the absence of external forces). The acceleration a is in the direction of the force and proportional to its strength, and is also inversely proportional to the mass being moved.
How does the engine facilitate the propelling force?. When the rocket engines on the starship NO-PAIN-NO-GAIN are suddenly turned off, while traveling in empty space, the starship will. In the absence of external forces, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with a constant velocity.
It continues to move until the handle accelerates it to a stop, which only happens as the head moves downward. B) An object in uniform motion in the absence of external force continues to move in the same direction. Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g.
Force causes objects to start moving. It is a very fundamental law of nature, and at some level, no one really knows why it’s true. The net force can not come from the object itself.
External forces are forces caused by external agent outside of the system. Science · Physics library · Forces and Newton's laws of motion · Newton's laws of motion What is Newton's first law?. Newton's First Law Of Motion Says That In The Absence Of External Forces, A Moving Object Has No Acceleration, Which Means The Magnitude And Direction Of The Velocity Are Constant.
This is what Newton's First law states " A body remains in a state of rest or uniform motion, unless it is acted upon by an external force. To determine what part should be considered external and internal, mechanical system should be clearly defined. In the absence of forces, ("body") at rest will stay at rest, and a body moving at a constant velocity in a straight line continues doing so indefinitely.
In the simplest case, a force applied to an object at rest causes it to accelerate in the direction of the force. The tendency of an object to conserve its mechanical energy is observed whenever external forces are not doing any overall work.If the influence of friction and air resistance can be ignored (or assumed to be negligible) and all other external forces are absent or merely not doing work, then the object is often said to conserve its energy. Note that this law also deals with "net external forces" and if the net external force is zero, the object will have.
When a car begins to move forward, what force makes it do so?. It could be the sum of two forces or more than two forces. In the absence of all external forces, an object's velocity remains constant.
Carbon dioxide).A gas mixture, such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. It is a consequence of the law of conservation of energy angular momentum is conserved, such that mvrmr2 constant If an object is held to move in a circular path (an. Gradually speed up until it reaches its terminal velocity e.
So moving a force means you have to “add” a new couple. The Example of Pendulum Motion. The apple now has less gravitational potential energy.
The Earth's orbit requires a bit more explanation. C) move slower and slower until it finally stops. However, if the object is already in motion, or if this situation is viewed from a.
I push on a book, and it doesn't yet move. Objects may or may not have forces acting on them. TRUE - If an object has momentum, then it is moving.
1 In the absence of a net force, a moving object will A slow down and eventually stop B stop immediately C turn right D move with constant velocity E turn left. If an object is moving with uniform velocity, it has no NET force acting on it. An object that is not moving won't start moving until some force is placed upon it.
Like all objects that do or can move, NASA Sounding Rockets obey Newton's Laws of Motion. The Earth's 24 hour rotation is maintained by the conservation of angular momentum. Which of the following forces exists between objects even in the absence of direct physical contact?.
It states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. 1)In the absence of any net external force a moving object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line.This is also known as t view the full answer. When the two objects are in relative motion we call it kinetic friction.
C) If an object is accelerating, a force is acting on it. It is the property of mass of the body which opposes a change. Momentum is momentum and energy is energy.
The net force adds up to zero. This law can be best observed in space, far from the gravity of a star or planet, where there is no friction or air resistance. Velocity is a vector quantity which expresses both the object's speed and the direction of its motion;.
In the absence of any forces, no force is required to keep an object moving. (The internal forces actually cancel, as we shall see in the next section.) You must define the boundaries of the system before you can determine which forces are external. If only one force acts upon an object, then this one force would be the net force.
Share this Share on Facebook Tweet on Twitter Plus on Google+ « Prev Question. An object can move even when no force acts on it. Sometimes the system is obvious, whereas other times identifying the boundaries of a.
Move with constant velocity in a straight line b. The object is not in motion, so there must be force that balances my push. A More Complete Description Of An Object Moving Along A Line Includes Its Accelera- Tion, Which Is The Rate Of Change Of The Velocity;.
A) If a single force acts on an object, the object accelerates. Slow down and eventually come to a stop d. B) If an object isn't moving, no external forces act on it.
MOVING A FORCE OFF OF ITS LINE OF ACTION When a force is moved, but not along its line of action, there is a change in its external effect!. The elevator is moving up at constant speed. What is the tension in the string?.
Newton (N) In this section we have introduced the quantity normal force, which is represented by the variable N N size 12{N} {}. Move with constant velocity in a circular orbit c. If a single force acts on an object, the object accelerates.
This is the law of conservation of momentum. This law is called the law of inertia. Friction represents an external force acting on the object, just as your push is an external force.
This can take the form of a collision. In%the%absence%of%an%external%force,%amoving%objectwill% (A)%stop%immediately%%%%%(B)%slow%down%and%eventually%come%to%astop% (C)%move%faster%and%faster%%%%%(D. The principle of conservation of momentum states:.
Normal Force (N) vs.
Www Franklinboe Org Cms Lib Nj Centricity Domain 705 Pfc ebook Pdf
Www Mrliddell Com Uploads 5 7 9 4 Chapter 6 Momentum Pdf
Newton S First Law Of Motion Zona Land Education

Physics Chapter 4 Forces And The Laws Of Motion Flashcards Quizlet

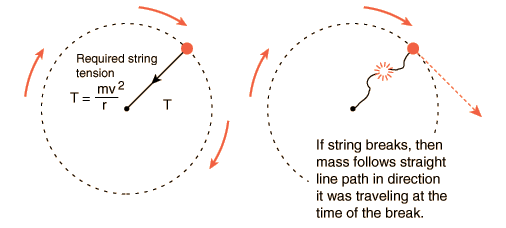
Lab 5 Uniform Circular Motion

6 3 Centripetal Force University Physics Volume 1

Bansal Classes 11th Standard Physics Dpps dc Pdf By S Dharmaraj Issuu
Newton S Laws
4 2 Newton S First Law Of Motion Inertia Physics Openstax

What Is Newton S Second Law Of Motion Isaac Newton The Guardian

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed
Www Stocktonusd Net Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 3227 8th grade science textbook Pdf
2
Newton S First Law Of Motion Zona Land Education

Intuitive Physics Current Research And Controversies Trends In Cognitive Sciences
Cdn2 Hubspot Net Hubfs Human movement excerpt Pdf T

Ap Physics 1 Review Of Forces And Newton S Laws Video Khan Academy
Solved In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Obje Chegg Com

Pdf A Case Study Of A Novice College Student S Alternative Framework And Learning Of Force And Motion

Module 10 Force And Motion Edited

Chapter 4

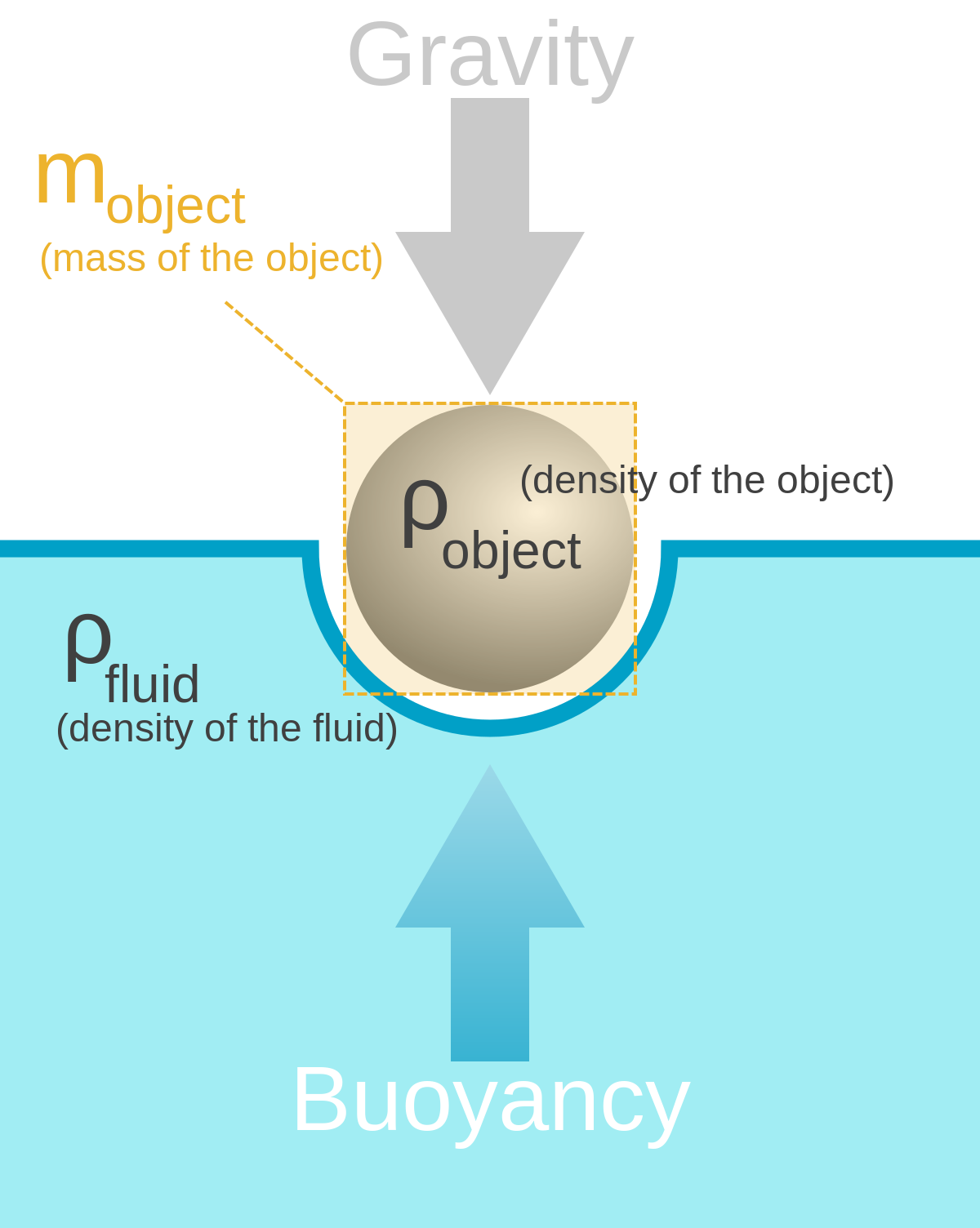
Buoyancy Wikipedia

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Unbalanced Forces And Motion Video Khan Academy
Www Smcisd Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 1073 Unit hw momentum collisions ans key Pdf
Ask The Physicist
Www Unit5 Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 3109 Dataid Filename Spr Exam Review Qs 16 Key Pdf

Module 10 Force And Motion Edited
Www Wcpss Net Cms Lib Nc Centricity Domain 53 Physic Textbook Compressed Pdf

Module 10 Force And Motion Edited
Cbse 9 Physics Cbse Work And Energy Ncert Solutions
Www Mrliddell Com Uploads 5 7 9 4 Chapter 6 Momentum Pdf
2

Analysis Of Situations In Which Mechanical Energy Is Conserved

Physics Puzzles With Answers
How Things Work Phys1055 Revealing The Magic In Everyday Life Phys0612

Pdf Student Misconceptions About Force And Acceleration In Physics And Engineering Mechanics Education
Newton S Laws Of Motion Article Forces Khan Academy

Quiz 2 Binka Diagram Quizlet
Www Franklinboe Org Cms Lib Nj Centricity Domain 705 Pfc ebook Pdf
2
2
Newton S Laws
Apcentral Collegeboard Org Pdf Ap Physics 1 Course And Exam Description Pdf
Silo Tips Download Chapter 5 The Laws Of Motion

Conceptual Physics Daily Ppt Download
Http Kirkmcd Princeton Edu Examples Ph101 09 Labs Ph101 Lab Manual 09 Pdf

Unbalanced Forces And Motion Video Khan Academy
2

Physics Puzzles With Answers
Http Kirkmcd Princeton Edu Examples Ph101 09 Labs Ph101 Lab Manual 09 Pdf
2

In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Will A Stop Immediately B Course Hero

Chapter 4
Www Mrliddell Com Uploads 5 7 9 4 Chapter 6 Momentum Pdf

6 3 Centripetal Force University Physics Volume 1

Chapter 4
2

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed
Ask The Physicist
2

The Biggest Myth About Black Holes

Physics Puzzles With Answers

The Tendency Of An Object To Resist Change In Its Motion Is Known As

Analysis Of Situations In Which Mechanical Energy Is Conserved
Buoyancy Wikipedia

Which Of The Following Options Is Correct In The Absence Of Any External Forces A Moving Object Will A Slow Down And Eventually Come To A Stop B Gradually Speed Up Until

In The Absence Of An External Force A Moving Object Will A Stop Immediately B Course Hero
Http Www Physics Princeton Edu Mcdonald Examples Ph101 06 Ph101 Lab Manual 06 Pdf

Air Resistance And Free Fall Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

In Which Case Of A Moving Body Force Is Not Needed

Pdf Student Misconceptions About Force And Acceleration In Physics And Engineering Mechanics Education

Solved Test 2b General Physics I Physies 2110 03 94 Fall Chegg Com
2
Http Web Mit Edu Yczeng Public Workbook 1 full Pdf
Schoolwires Henry K12 Ga Us Cms Lib Ga Centricity Domain Revised physics 1 class notes Pdf

Module 10 Force And Motion Edited
Www Tafths Org Ourpages Auto 18 1 22 Ck12 full text Pdf
Scholar Dickinson Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 1000 Context Vpythonphysics

Q Tbn 3aand9gct9uogdumkkzmtebqnygej5fbqepun7owku6w Usqp Cau
Www Kau Edu Sa Files Subjects Chapter 6 Pdf
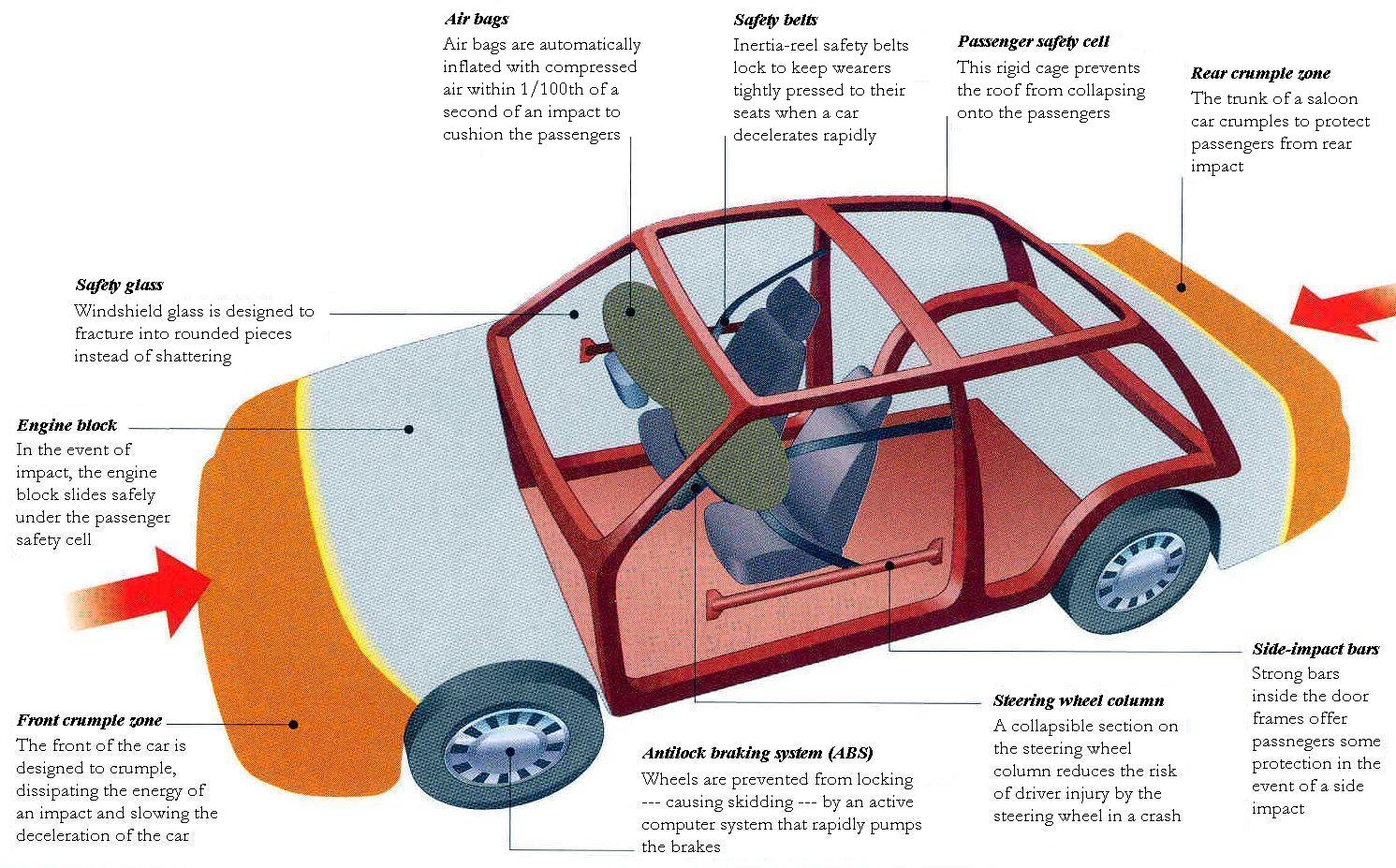
How Things Work Phys1055 Revealing The Magic In Everyday Life Phys0612
Scholar Dickinson Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 1000 Context Vpythonphysics
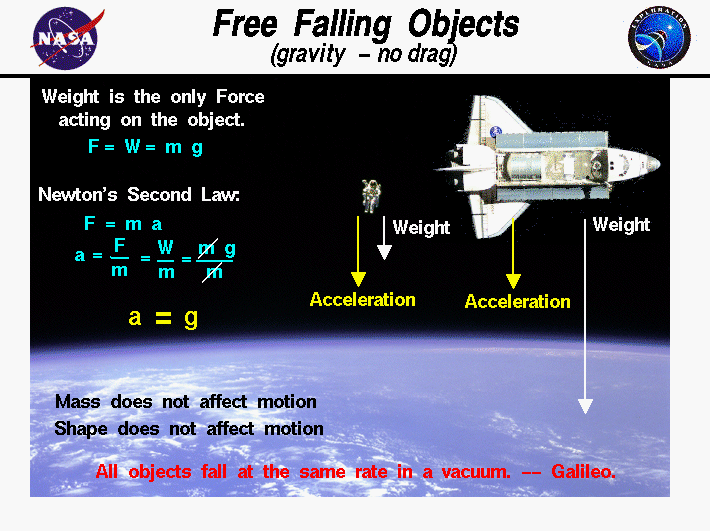
Free Falling Objects

The Tendency Of An Object To Resist Change In Its Motion Is Known As

Force Mass Acceleration Newton S Second Law Of Motion Live Science
4 2 Newton S First Law Of Motion Inertia Physics Openstax

Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces Physics
Http Assets Pearsonglobalschools Com Asset Mgr Current 1315 Gian Pp7 Sample Chapters4and6 Pdf
Http Web Mit Edu Yczeng Public Workbook 1 full Pdf

Inertia And Mass

The Brain Adjusts Grip Forces Differently According To Gravity And Inertia A Parabolic Flight Experiment Abstract Europe Pmc

Chapter 9 Gravity And Some Satellite Motion Universal Law Of Gravitation Universal Gravitational Constant G Inverse Square Law Weight And Weightlessness Ppt Download
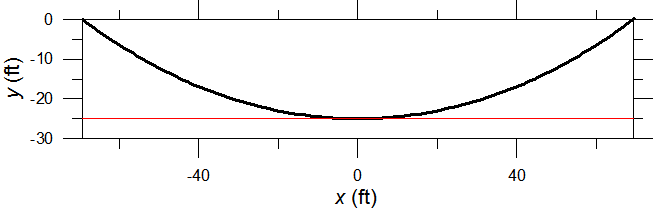
Ask The Physicist



